The context of ITIL 4 has greater emphasis on the business and technology world, how it works today, and how it will work in the future with Agile, DevOps and digital transformation.
There are four certification designations within the ITIL 4 scheme:
- ITIL 4 Foundation
- ITIL 4 Managing Professional designation, comprised of four modules:
ITIL 4 Specialist Create, Deliver and Support (CDS)
ITIL 4 Specialist Drive Stakeholder Value (DPI)
ITIL 4 Specialist High-velocity IT (HVIT)
ITIL 4 Strategist Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI) – Universal module
- ITIL 4 Strategic Leader designation, comprised of two modules:
ITIL 4 Strategist Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI) – Universal Module
ITIL 4 Leader: Digital and IT Strategy.
- ITIL 4 Master
No, once you pass all four modules you will automatically receive the ITIL 4 Managing Professional designation.
Candidates must be certified in ITIL 4 Foundation and all four modules that comprise the ITIL 4 Managing Professional designation.
Candidates must be certified in ITIL 4 Foundation and both modules that comprise the ITIL 4 Strategic Leader designation. Candidates must also be able to demonstrate that they have at least three years’ minimum of managerial experience.
AXELOS has not mandated training for ITIL 4 Foundation, so you are able to self-study. However, candidates are encouraged to attend an accredited training course to fully understand the new material.
For all modules in the ITIL 4 Managing Professional and ITIL 4 Strategic Leader designations (including the ITIL 4 Managing Professional Transition module) training is mandatory to enable candidates to fully understand the new material.
ITIL 4 consists of the following core guidance publications:
- ITIL 4 Foundation
- ITIL 4 Specialist: Create, Deliver and Support (CDS) ● ITIL 4 Specialist: Drive Stakeholder Value (DPI)
- ITIL 4 Specialist: High-velocity IT (HVIT)
- ITIL 4 Strategist: Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI)
- ITIL 4 Leader: Digital and IT Strategy.
Yes, candidates should receive separate certificates, as follows:
- ITIL 4 Foundation certificate
- Individual certificates for each completed ITIL 4 Managing Professional and/or ITIL 4
Strategic Leader modules
- A certificate for achieving the ITIL 4 Managing Professional and/or ITIL 4 Strategic
Leader designations
Individual certificates for the ITIL 4 Managing Professional and/or ITIL 4 Strategic designation(s) will be awarded to candidates once all training has been completed and candidates have passed the required exams for that designation.
COBIT is a framework for the governance and management of enterprise information and technology, aimed at the whole enterprise. COBIT defines the components and design factors to build and sustain a best-fit governance system.
The globally recognized COBIT 2019 Framework helps ensure effective EGIT, facilitating easier, tailored implementation—strengthening COBIT’s continuing role as an important driver of innovation and business transformation.
- COBIT 2019 Framework: Introduction and Methodology – an introduction to the key concepts of COBIT 2019.
- COBIT 2019 Framework: Governance and Management Objectives – comprehensively describes the 40 core governance and management objectives, the processes contained therein, and other related components. This guide also references other standards and frameworks
- COBIT 2019 Design Guide: Designing an Information and Technology Governance Solution – this guide explores design factors that can influence governance and includes a workflow for planning a tailored governance system for the enterprise.
- COBIT 2019 Implementation Guide: Implementing and Optimizing an Information and Technology Governance Solution – this title represents an evolution of the COBIT 5 Implementation guide and develops a road map for continuous governance improvement. It may be used in combination with the COBIT 2019 Design Guide.
As part of ISACA’s commitment to provide optimal value for its members, the PDF download of the following four (4) core COBIT 2019 publications will be free to members.
One of the guiding principles applied throughout the development of COBIT 2019 was to maintain the positioning of COBIT as an umbrella framework. Thus, COBIT continues to align with a number of relevant standards, frameworks and/or regulations. The COBIT 2019 includes references and aligns to concepts originating in other sources (e.g., other IT standards and frameworks).
Training to support the release of the updated guidance is available for Foundation (1-day Bridge course for COBIT 5 Foundation certified candidates and 2-day class for candidates new to COBIT). It is also available for COBIT Design & Implementation, a 3-day course presenting advanced concepts on how to design and implement a governance system.
ISACA will continue to support the many governments and non-government organizations that have implemented COBIT 5 since its inception in 2012. All COBIT 5 guidance (and derivative products) will continue to be available for electronic download or purchase. Additionally, all COBIT 5 products, resources and related training programs will remain available (along-side COBIT 2019).
ISACA will continue to support the accreditation and delivery of the COBIT 5 training and certificate schemes. COBIT 5 training will continue to live alongside COBIT 2019 training, delivered through our network of accredited training partners or ISACA’s on-site team.
COBIT 2019 offers greater flexibility and openness to enhances the currency and relevance of COBIT.
The introduction of new concepts such as focus areas and design factors allow for additional guidance for tailoring a governance system to the enterprise’s needs.
Updated alignment to global standards, frameworks and best practices enhances the relevancy of COBIT.
An “open-source” model will allow the global governance community the ability to inform future updates by providing feedback, sharing applications and proposing enhancements to the framework and derivative products in real-time, with further COBIT evolutions released on a rolling basis.
New guidance and tools support the development of a best-fit governance system, making COBIT 2019 more prescriptive.
A Management System describes and demonstrates your organisation’s approach to managing well parts of your operations. It will help you identify and address the threats and opportunities around your valuable information and any related assets. That contributes to protect your organisation from security breaches and to shield it from disruption when they do happen. It will help to ensure a relevant level of quality is defined, agreed, and implemented.
Key business benefits
- Help you win new business and enter new sectors
- Strengthen your relationship with your existing customers
- Build your organisation’s brand and reputation
- Protect your business from security breaches
To achieve these benefits (and more!), you’ll need a quick and easy way of demonstrating your policies, procedures, and controls with your Management System. That’s why many organisations choose to go for ISO compliance or certification. Achieving the standards is a very effective way of proving the ongoing excellence and effectiveness within your organisation. Typical ISO standards organizations choose to certify with are 9001 (Quality Management), 14001 (Environment), 20000 (Service Management), 22000 (Food and Safety), 22301 (Business Continuity), 27001 (Information Security), and 37001 (Anti-Bribery), to name a few.
Our expert support teams can work with organisations of every type, size, and level of ISO standard know-how. We can also provide a platform to achieve and manage this Management System in line with any ISO standards faster and meet regulations like GDPR and others.
Let’s take the Information Security Management System (ISMS) and look at how we can help you. The approach would be very similar if it applies to another ISO Management System or to an integrated Management System (aligned to more than one ISO Management System standard).

What does an ISMS do?
Your information security management system can help support your business in many ways. You will find that an effective ISMS can:
- Safeguard your organisation’s information assets
- Make it easy to demonstrate how secure your information is
- Show how seriously your organisation takes information security
- Help you stay ahead of new information security risks and opportunities
What does an ISMS include?
To achieve ISO 27001 compliance or certification, you need a fully functioning ISMS that meets the standard’s requirements. It will define your organisation’s information assets, then cover off all the:
- Risks your organisation’s information assets face
- Measures you’ve put in place to protect them
- Guidance to follow
- Actions to take when your information assets are threatened
- People responsible for or involved in every step of the information security process
Your ISMS should meet your organisation’s unique needs, taking account of:
- How your organisation, its stakeholders and customers work in practice?
- What sort of risk appetite you and they have?
- The wider contexts that affect you all.
Don’t start from scratch
We’d advise to first conducting a gap analysis, closing many common gaps immediately. Your organisation will most definitely already have elements of the ISMS in place, start from there.
Your ISMS needs to be something you can manage and update on an ongoing basis; that can be very difficult with multiple static documents. Look for a solution that enables you to create, communicate, control, and collaborate with ease – this will ensure you can approach your ISO 27001 audits with confidence. We can help with this too.
What you’ll need to implement your ISMS
The 7 items below will be required to successfully implement an ISMS.
- ISMS implementation resource
Creating or upgrading an ISO 27001 compliant or certified information security management system can be a complex, challenging process. To implement it successfully, you’ll need a clearly defined manager or team with the time, budget and knowhow needed to make your ISMS happen. And once it’s up and running your business will need to have the right ISMS governance processes in place.
Our experts can guide you to first time ISO 27001 success. We also suggest governance processes and procedures too.
- Systems and tools for implementation and ongoing management
An effective information security management system draws on and manages many different resources. As well as its data they can include your organisation’s software and hardware, its physical infrastructure and even its staff and suppliers. You’ll need to implement the right processes, systems, and tools to guide and oversee them all through your ISMS. That kind of systematic approach guarantees effective risk management for your whole organisation.
We can recommend a platform including a wide range of bespoke information security support systems, ranging from our context-specific Virtual Coach to a full suite of implementation management tools.
- Actionable policies and controls that will work in practice
Your information security management system will tell your colleagues, suppliers, and other stakeholders how to protect your information assets and what to do when they’re at risk. Those information security practices and procedures must be defined in clear, widely understood, and easy to act on policies and controls. That way the benefits of your ISMS will be widely and easily understood, and its integrity assured.
Our pre-loaded Adopt, Adapt, Add Content gives you actionable policies and controls that take you 77% of the way to your goal before you’ve even begun.
- Staff communications and engagement mechanisms
ISO 27001 requires that your organisation lives and breathes your information security management system. So, your colleagues and other interested parties need to know about your ISMS, understand why it’s so important and have a clear sense of their information security responsibilities. If an ISMS just sits there gathering dust, it won’t protect anything! Effective engagement tools and procedures are essential. You might even need to run some information security training courses.
Our Policy Packs make it easy to share specific policies and controls with everyone who needs to know about and follow them, across your organisation and beyond it.
- Systems and tools for supply chain management
Your information security management system will extend beyond your organisation. Your suppliers and other third parties probably hold or handle valuable data on your behalf. Complying with ISO 27001 can mean making sure they comply with your ISMS too. And to assure your organisation’s integrity you’ll need to protect yourself against any information security issues or challenges their use of your data could create.
Our approach gives you everything you need to assess your supply chain information security needs, then put the right precautions in place to meet them.
- Certification activity and working with external auditors
If you’re going for full ISO 27001 certification, you’ll need to find an accredited independent certification body for your ISMS. They’ll take you through a two-stage certification process. Then they’ll return for regular update audits during the three-year life of your ISO 27001 certification. To comply with the standard, you’ll need to take your ISMS through regular internal audits too.
We can guide you to ISO 27001 certification, make showing your external auditors how effective your ISMS is a simple task, simplify internal audits and help you manage recertification too.
- Ongoing ISMS operation and improvement resource
An effective information security management system is always on and always alert. It evolves to match its organisation’s growth and development and meet constant new information security challenges. And it quickly picks up and corrects any of its own glitches or errors, using them as data to drive constant improvement. After all, risk assessment and response never ends.
We provide a full suite of easy-access ISMS management and improvement tools and procedures, plus guidance on everything from engaging senior managers to sorting out your risk treatment plan. We can also fulfil ISMS operational roles that you may not have the resources for.
The traditional consultancy model of large teams on site for weeks at a time is out of sync with today’s culture. Clients want access to the very best people, on their terms.
Fifalde offers Management Consultancy as a service (MCaaS). Our clients get the advice and support they need, when they need it, from enthusiastic and committed professionals – delivered virtually.
MCaaS engagements can be used to provide support and mentoring, for specific projects, for people who are new in their role, and for anyone involved in a digital transformation program. If a project is going off course, our consultants can get you back on track, fast.

Working with a virtual management consultant
is simple
You start with a kick-off meeting, where you get to know each other. You will agree what you want to achieve and a draft timetable for your meetings. After the meeting, your management consultant will confirm the objectives in writing and set up your calendar appointments.
You can use virtual consultancy time for meetings, or to ask your management consultant to review documents and plans. Your timetable is flexible, subject to your and your management consultant’s availability.
The future of consultancy is virtual
Have you ever…
- Completed a training course and then wondered where to start
- Wished you could have just a short conversation with someone who’s done it all before
- Felt like your organization could be doing things better, but not know how
- Wanted some ongoing support during a long-term project, but not on a full-time basis
Imagine having the best management consultants in the industry at your fingertips. Choose who you work with, for how long, and how often. Virtual management consultants give you flexible help when you need it most.
Consultancy packages
Typical packages include:
- Building an improvement plan – define measurable steps to meet your long-term goals
- Change enabler – support during an organizational change such as a restructure or digital transformation
- 60-minute support – to answer that urgent question, or to help you get to know our consultants
- Emergency assistance – who do you call when something goes wrong?
- Industry expert – work with the best of the best in fields like process improvement, cybersecurity, organizational change, and agile management
- Mentoring – regular support if you’re new in post or working in a new way
- Rapid assessment – a targeted evaluation of what’s in place and recommendations for improvements
What is Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)?
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the U.S. define ZTA as: “an enterprise cybersecurity architecture that is based on zero trust principles and designed to prevent data breaches and limit internal lateral movement”.
ZTA pushes organizations to start with denying access to applications and data by default. Threat prevention is achieved by only granting access to networks and workloads utilizing policy informed by continuous, contextual, risk-based verification across users and their associated devices. That means that the organization should start with acknowledging that all entities are untrusted by default, least privilege access is enforced (risk-based assessment), and comprehensive security monitoring is implemented.

A ZTA must first be based on guiding principles, workflows, system design thinking, and operations. A major aspect will be the risk assessment approach.
Key guiding principles to achieve a ZTA are:
- All data sources and computing services are considered resources
- All communication is secured regardless of network location
- Access to individual enterprise resources is granted on a per-session basis
- Access to resources is determined by dynamic policy
- The enterprise monitors and measures the integrity and security posture of all owned and associated assets
- All resources authentication and authorization are dynamic and strictly enforced before access is allowed
- The enterprise collects as much information as possible about the current state of assets
For most organization, achieving a ZTA is a journey, a journey that starts with the confirmation of which guiding principle applies to them. It continues with the identification of what you have as assets, the degree of protection each asset needs (based on how critical they are to the organization), the identification of the policies and controls and their implementation. It concludes with a thorough monitoring and continual improvement.
The figure below, a reproduction of the NIST ZTA Deployment cycle, depicts key aspects for achieving a ZTA. The first past is the knowledge of our organizational context and specifically our processes, systems, and key stakeholders. Once this is well understood, a proper risk assessment can be done.
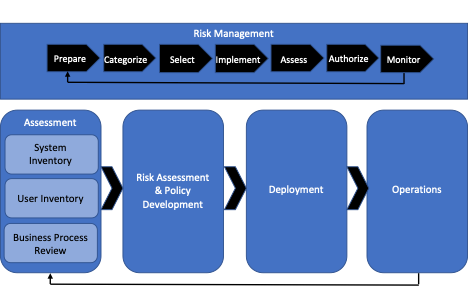
The risk assessment will be critical in defining the level of protection needed, from none to maximum level. This assessment will only be good if it is supported by a robust risk management process. When the level of protection for each asset is defined, we can proceed onto the identification of policies/controls. Finally, deployment onto operation of the approaches can start. We need to also highlight that just like any risk management process would include a feedback loop, the deployment of controls towards the achievement of ZTA also has a feedback loop, ensuring monitoring exists in operation and when applicable, continuous improvement can drive re-assessment of the organization’s context and restart the whole exercise.
The overall approach is not very complicated, but all organizations are different, and the path they will need to follow to achieve ZTA will then vary from one organization to another. Fifalde Consulting can help your organization to define your journey towards a proper Zero Trust Architecture.
Digital Transformation
True digital transformation requires evaluating and changing not just one, but multiple aspects of a business.
The most effective and beneficial digital transformations require changes across departments in the organization, at all levels—from the individual worker to the C-suite—and across all the connected business elements, such as processes, activities, and assets. It is a cultural change, people across the organization, and possibly outside of the organization, will be affected.
In most organizations, digital transformation starts with initiatives in customer-facing areas, such as marketing, sales, or support.
As your digital transformation efforts expand back into operations and internal processes, it’s important that you always continue your analysis with the customer as the starting point. Ultimately, every part of the business exists to serve its customers.
Aligning to best practices on Customer Journey and Customer Experience is key to the success.
Over the years we have developed an approach to guide us as we help customers with digital transformations. The approach is shown below.

The Approach
1. Context Discovery and Strategy Definition
Establish the project
Identify key stakeholders and their needs and drivers
Define strategic objectives
Define governance requirements and high-level governance framework
Define principles and policies
Define roles and responsibilities
Map existing services and sourcing environment
Assess the organization’s process capability and maturity
Understand the marketplace
Define how to manage organizational change
Initiate the business case Design the New Service Model
2. Design the service model
Sourcing approach
Governance model
Process model
Roles and responsibilities
Performance management
Technology strategy
Improvement approaches
Update the business case and obtain approval to proceed
3. Plan the Implementation
Proceed to detailed planning
Select implementation approach
4. Implement
Transition to the approve service model
5. Run and improve
Operate and maintain services
Monitor operations
Report on performance
Review performance against objectives
Conduct audits
Assess compliance
Identify improvements and obtain approvals to proceed
Initiate improvements
Let us help you with your digital transformation!
What is business continuity?
Business continuity is the process of identifying potential risks to your business and developing plans to ensure that your organization can continue to operate in the event of a disruption.
Why is business continuity important?
Every business will face unexpected challenges at some point, whether it’s a natural disaster, cyber-attack, or other unforeseen event. A well-thought-out business continuity plan can help companies weather the storm and get back on track quickly.
What does a business continuity plan involve?
A business continuity plan involves identifying potential risks to your business, assessing their potential impact, and developing a plan to mitigate those risks. This includes creating a communication plan to ensure that all stakeholders are informed and engaged in the process.
How can your business continuity practice help my organization?
Our business continuity practice is designed to help companies identify potential risks, assess their impact on business operations, and develop plans to mitigate those risks. We offer easy-to-implement solutions that can be customized to fit the unique needs of your organization, along with comprehensive training and ongoing support services.
How can I get started with improving my business continuity processes?
Don’t wait until disaster strikes to start improving your business continuity processes. Contact our team today to learn more about how we can help you keep your business running smoothly no matter what challenges may come your way. We’re here to help you protect your organization and ensure that it remains resilient in the face of unexpected even

How can I get started with improving my business continuity processes?
Don’t wait until disaster strikes to start improving your business continuity processes. Contact our team today to learn more about how we can help you keep your business running smoothly no matter what challenges may come your way. We’re here to help you protect your organization and ensure that it remains resilient in the face of unexpected even
Why should I measure the performance of my governance processes?
Measuring the performance of governance processes is important to ensure that they are effective in achieving their objectives and delivering value to stakeholders. Measuring the performance of governance processes requires identifying the objectives of the processes and defining relevant metrics that can be used to measure progress toward those objectives.
What should I start with?
First you must define the objectives of the governance management processes: Identify the specific goals that the governance processes are designed to achieve. For each goal, define the objectives (SMART) of the governance processes. Objectives could be related to improving compliance, reducing risks, enhancing decision-making processes, increasing transparency, and promoting accountability and they will confirm to which extend the goals are fulfilled.

What do I need to do once I have SMART objectives?
The next step is to identify relevant metrics: Once you have identified the objectives of the governance processes, identify the key performance indicators (KPIs) that can be used to measure progress toward those objectives. Metrics should be relevant to the objectives, measurable, and easy to collect and analyze. For example, if one of the objectives is to improve compliance, relevant metrics could include the number of compliance breaches, the frequency of audits, or the percentage of employees who complete compliance training.
Does it stop with the definition of the metrics?
Certainly not, to know what you should see from the metrics you need to establish targets: Set targets for each metric to provide a baseline for comparison. These targets should be realistic and achievable based on historical data or industry standards.
What do I do once my targets are defined?
Now you are ready to collect data, so you need to implement data collection and analysis practices: Collect and analyze data on the identified metrics to track progress toward the established targets. Regular data collection and analysis will provide insights into areas of success and areas that need improvement.
Is collection and analysis of the data the last step in measuring the performance of governance processes?
No quite, the last step consist of monitoring progress and adjust the processes: Continuously monitor progress and adjust the governance processes as necessary to ensure that the objectives are being met. Use the data collected to identify areas that require improvement and make changes to the process accordingly.
What are possible examples of governance process metrics?
Here are a few examples of governance process metrics that can be used to measure performance:
Compliance with regulatory requirements
Board diversity and independence
Timeliness of decision-making
Effectiveness of risk management and internal controls
Alignment of governance processes with organizational strategy
Stakeholder engagement and satisfaction
Transparency and disclosure of information
Cost efficiency of governance processes
Overall, by defining objectives and relevant metrics, setting targets, implementing data collection and analysis, and monitoring progress, you can effectively measure the performance of governance processes and make informed decisions about process improvements. By measuring governance processes performance with objectives and metrics, organizations can ensure that they are effective in achieving their goals and delivering value to stakeholders.
Why should my organization justify implementing an ISO management system?
Implementing an ISO management system can bring several benefits to your organization such as enhanced credibility and reputation, improve effectiveness and efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
How can our credibility or reputation be better by having an ISO management system?
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) standards are globally recognized and respected. By implementing an ISO management system, you demonstrate your commitment to meeting internationally accepted best practices and quality standards. This can enhance your organization’s credibility and reputation, giving you a competitive edge in the marketplace.
How would effectiveness and efficiency be improved?
ISO standards provide a systematic framework for managing various aspects of your organization. They help streamline processes, reduce waste, and improve overall effectiveness and efficiency. By implementing an ISO management system, you can identify and eliminate bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and enhance productivity.

Why would customer satisfaction improve by implementing and ISO management system?
ISO standards focus on meeting customer requirements and enhancing customer satisfaction. By implementing an ISO management system, you establish processes and procedures that ensure consistent delivery of high-quality products or services. This can lead to increased customer satisfaction, repeat business, and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
What are key other advantages of implementing an ISO management system?
ISO standards often align with regulatory requirements in various industries. Implementing an ISO management system can help your organization ensure compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards.
ISO management systems are built on the principles of continuous improvement. By implementing such a system, your organization embraces a culture of ongoing evaluation, learning, and refinement. This leads to a proactive approach to problem-solving, innovation, staying ahead of the competition, and continually aligned with business needs.
ISO standards include risk-based thinking and require organizations to assess and manage risks effectively. By implementing an ISO management system, you can identify potential risks, implement appropriate controls, and establish processes for risk monitoring and mitigation. This helps your organization reduce the likelihood and impact of adverse events.
It's important to note that the specific benefits may vary depending on the ISO standard you choose to implement (e.g., ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 14001 for environmental management, ISO/IEC 27001 for information security management, etc.). Consider evaluating the specific needs and goals of your organization to determine which ISO standard is most relevant and beneficial for your operations.
Could Fifalde Consulting help us in initiating the development and implementation of an ISO management system?
Sure, we can, we have been involved with management system development and implementation since the start of the company in 2004. Since then, we have maintained a continuous involvement in the development of quite a few of these standards. We have experts that can help you from the beginning, definition and confirmation of your context, the planning, the development or improvement of your processes, the development of a performance management system, the implementation and preparation to be certified. Contact us for more details.
Organizations often face a plethora of best practices, ranging from simple to complex, which can be overwhelming and hinder their belief in making meaningful improvements. The key to improvement lies in understanding service consumers, their expectations, and the best ways to deliver services. Additionally, service providers must ensure that their services are provided optimally and have plans in place to continuously improve them.
Before embarking on service improvement, organizations must have a well-defined strategy for designing and delivering services. Monitoring performance is equally crucial to identify weak areas and address them logically and efficiently based on available resources.
In service management, the service desk plays a critical role as the first point of contact for users. Optimizing the service desk can significantly enhance the service offering. Borrowing from the "shift left" practice in software development, organizations can diagnose and solve problems at the front-end of the process rather than waiting for major incidents to occur. This approach reduces defects, saves resources, and improves overall performance.
Applying the "Shift left" practice to the service desk can empower less technically experienced resources to resolve issues earlier, reducing escalations, improving first-time fix rates, cutting service costs, and enhancing customer experience. For example, building core diagnostic questions into the user self-help portal can encourage users to apply fixes independently.
To embark on a successful "Shift left" program, align workflows, roles, responsibilities, and performance systems to support and reward these changes. Here are some basic best practices to consider when improving the service desk:
- Define relevant metrics and gather data for analysis.
- Focus on high-value targets for initial improvement.
- Empower service desk employees with policies, training, and tools.
- Establish clear escalation triggers.
- Test the new operational model before implementation.
- Continuously measure performance.
- Scale improvements based on performance results.

At Fifalde, our experienced specialists help organizations optimize their service offerings through a systematic approach of discovery, assessment, analysis, improvement planning, implementation, and validation.
We believe in empowering organizations to sustain improvement by providing them with the necessary resources, processes, tools, and partnerships.
Through training, we ensure that our clients can continue to enhance their services independently and create a more sustainable improvement process.
The Service Configuration Management practice primarily supports these practices:
- Incident Management,
- Problem Management,
- Change Control,
- Release Management,
- Service Level Management,
- Financial Management of Services,
- Service Continuity Management,
- Availability Management,
- Capacity and Performance Management, and
- Service Desk.
Additionally, this process also supports these practices:
- Asset Management,
- Project Management,
- Supplier Management,
- Continual Improvement, and many others.
Considering the main practices related to or directly supported by the Service Configuration Management practice, it is evident that the operational aspect is the primary focus.
Implementing a Service Configuration Management practice is complex and requires a significant number of resources for the organization. Therefore, it is essential to ensure proper scope management during implementation. A phased approach is recommended, with the operational environment being a top priority. Furthermore, to ensure project success, it is crucial to have an automated solution for managing configuration items.
Including environments such as development, testing, or training introduces complexity that could jeopardize the project’s success. These environments should be considered secondary and assessed based on the need and impact. It’s vital to link benefits to project goals and objectives and identify impacts to define scope and prioritize activities.

Given the complexity of implementing the Service Configuration Management practice, reducing risks throughout the project lifecycle will contribute to its success. Thus, it’s important to use the organization’s governance principles as a starting point and reference.
If these principles don’t exist, they should be defined. Starting from the Service Catalog is also recommended, prioritized based on business needs.
Lastly, considering security and business continuity criteria will prioritize aspects of the Service Configuration Management practice for initial implementation. Existing organizational issues can also help define the implementation scope.
Throughout this scoping process, always keep in mind the methods, preferably automated, that will be in place to maintain these configuration items.
Following these recommendations will help facilitate the success of a Service Configuration Management practice implementation project. Always remember that business needs are critical in identifying the implementation direction. These business needs will drive the necessity for governance and controls, which in turn will guide the practice’s definition. Lastly, prioritize critical services and problematic operational scenarios.
Starting a Transformation Management Office (TMO) in a new organization requires careful planning and execution. The TMO will be responsible for driving and overseeing transformational initiatives, so it's essential to set it up effectively.
Here's a step-by-step approach to help you get started:
- Understand your Organization's Goals and Culture: Before setting up your TMO, ensure you have a deep understanding of your organization's strategic objectives, goals, and its culture. Transformation initiatives should align with your organization's overall vision.
- Define the TMO's Purpose and Scope: Clearly define the TMO's purpose, objectives, and the scope of its responsibilities. Determine whether it will focus on specific areas of transformation (e.g., digital transformation, process optimization) or take a broader approach.
- Build a Skilled Team: Assemble a team with diverse skills and expertise relevant to the organization's transformation needs. Look for individuals who understand organizational change management, project management, data analysis, communication, and organizational behavior.
- Establish Governance and Structure: Define the TMO's governance framework and structure. This includes outlining reporting lines, roles and responsibilities, authorities, decision-making processes, and accountability measures.
- Secure Executive Sponsorship: Obtain support and sponsorship from top-level executives. A well-established TMO requires buy-in from leadership to ensure that transformation initiatives are adequately funded and prioritized.
- Identify Key Transformation Initiatives: Collaborate with relevant stakeholders, including subject matter experts, to identify transformation initiatives that align with the organization's goals. These initiatives should have a clear business case and measurable outcomes.
- Develop a Transformation Roadmap: Create a detailed transformation roadmap that outlines the sequence of initiatives, timelines, resource requirements, and interdependencies. This roadmap will guide your TMO's efforts over time and be a good tool for communication on progress.
- Establish Metrics and KPIs: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure the success of transformation initiatives. Regularly monitor and report progress to stakeholders.
- Implement Organizational Change Management Practices: Incorporate change management principles into the TMO's approach. Ensure that the organization is prepared for and receptive to the changes introduced through transformation initiatives.
- Promote Collaboration and Communication: If not already a reality in your organization, foster a culture of collaboration and open communication. The TMO should

11. Provide Training and Support: Offer training and support to employees who will be involved in or affected by transformation initiatives. Help them acquire, as soon as possible, the skills and knowledge needed to embrace the changes.
12. Iterate and Adapt: Continuously assess the effectiveness of your TMO and its initiatives. Be prepared to adapt the approach based on feedback and changing organizational needs.
13. Celebrate Achievements: Recognize and celebrate the achievements and milestones reached through successful transformation efforts. Positive reinforcement can motivate employees and boost engagement.
14. Learn from Failures: Acknowledge that not every initiative will be a resounding success. Embrace failures as opportunities to learn and improve future transformation endeavors.
15. Evolve and Scale: As your TMO gains experience and credibility, consider expanding its scope or scaling it to address broader organizational transformation challenges.
Remember that building a Transformation Management Office is an ongoing process. It requires continuous improvement, collaboration, and adaptability to effectively drive organizational change and achieve long-term success.
If you need help implementing or improving your TMO, contact us, our team of specialists will be happy to help you.
What is customer experience?
Customer experience refers to the overall perception and interaction that customers have with a business or brand throughout their entire journey. It encompasses every touchpoint and interaction a customer has, starting from the initial awareness or discovery of a product or service, through the purchase process, and continuing even after the sale.
Customer experience is shaped by various factors, including the quality of products or services, ease of use, customer service interactions, website usability, packaging, delivery, and post-sales support. It’s important to note that customer experience is not limited to a single interaction but rather encompasses the entire customer lifecycle.
A positive customer experience involves meeting or exceeding customer expectations at every stage of the journey. It focuses on providing a seamless and satisfying experience that leaves customers feeling valued, understood, and loyal to the brand. This often leads to increased customer satisfaction, repeat business, positive word-of-mouth recommendations, and customer advocacy.
Businesses that prioritize customer experience aim to understand their customers’ needs, preferences, and pain points. They invest in strategies and processes to enhance customer interactions, improve satisfaction, and build long-term relationships. This may involve personalizing interactions, streamlining processes, ensuring prompt and efficient customer service, and leveraging technology to enhance the overall experience.
In summary, customer experience is the sum of all the interactions, perceptions, and emotions that customers have with a business. It plays a crucial role in shaping customer satisfaction, loyalty, and the overall success of a brand.
What is customer journey?
The customer journey, also known as the buyer's journey, refers to the series of steps or stages that a customer goes through when interacting with a business or brand. It maps out the entire process from the initial point of awareness or consideration to the final purchase decision and beyond.
The customer journey typically consists of the following stages:
- Awareness: The customer becomes aware of a particular product, service, or brand through various channels such as advertising, word-of-mouth, or online research.
- Consideration: The customer starts actively considering the options available to fulfill their needs. They gather information, compare different products or services, read reviews, and evaluate the potential solutions.
- Decision: The customer narrows down their options and makes a final decision on which product or service to purchase. This stage often involves comparing prices, features, warranties, and other factors that influence the purchase decision.
- Purchase: The customer completes the transaction and acquires the chosen product or service. This could be done online, in-store, or through other channels, depending on the business.
- Post-purchase: After the purchase, the customer evaluates their experience with the product or service. They may provide feedback, seek support if needed, and develop perceptions about the brand based on their experience.
Understanding the customer journey is crucial for businesses as it helps them identify opportunities for improvement, enhance customer experiences, and increase customer satisfaction. By mapping out the customer journey, businesses can identify touchpoints where they can provide additional value, address pain points, or deliver personalized experiences.
It's important to note that the customer journey is not a linear process and can vary across different industries, products, and customer segments. It can be influenced by factors such as marketing efforts, customer service interactions, online experiences, and word-of-mouth recommendations. Therefore, businesses should continuously analyze and adapt their strategies to align with the evolving customer journey and changing customer expectations.

What is Customer Service Excellence?
Customer Service Excellence refers to the highest level of service and support provided to customers that goes above and beyond their expectations. It involves consistently delivering exceptional service and creating positive experiences for customers throughout their interactions with a business.
Customer Service Excellence is characterized by the following key principles:
- Customer-centricity: Placing the customer at the center of all interactions and decision-making processes. This involves understanding their needs, preferences, and expectations, and tailoring the service accordingly.
- Responsiveness: Being prompt and attentive in addressing customer inquiries, concerns, and requests. Responding to customer queries in a timely manner and providing efficient solutions contribute to a positive service experience.
- Empathy and Understanding: Demonstrating empathy towards customers' concerns and showing understanding of their unique situations. Listening actively, being patient, and demonstrating genuine care can enhance the customer service experience.
- Knowledge and Expertise: Possessing comprehensive knowledge about products, services, and relevant information. Customer service representatives should be well-trained and equipped with the necessary expertise to provide accurate and helpful information to customers.
- Personalization: Offering personalized service and tailoring interactions to the individual customer. Understanding and acknowledging customers' preferences, history, and specific needs can create a more customized and memorable experience.
- Proactive Communication: Anticipating customer needs and providing proactive communication and support. Keeping customers informed about relevant updates, offering assistance, and being proactive in resolving issues contribute to a positive service experience.
- Continuous Improvement: Striving for ongoing improvement in customer service processes and practices. Collecting customer feedback, analyzing trends, and implementing changes based on customer insights helps to enhance service excellence over time.
Customer Service Excellence is not limited to front-line interactions but encompasses the entire customer journey, including pre-sale, during-sale, and post-sale interactions. It aims to build strong customer relationships, foster loyalty, and generate positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
Businesses that prioritize Customer Service Excellence often invest in training their employees, implementing effective customer service systems and processes, and fostering a culture of customer-centricity throughout the organization. By consistently delivering exceptional service, businesses can differentiate themselves from competitors, create long-term customer relationships, and drive business success.
What is the user experience?
User experience (UX) refers to the overall experience that users have when interacting with a product, system, or service. It focuses on how users perceive, feel, and interact with a particular interface or design, whether it's a website, application, software, or physical product.
UX encompasses various elements, including usability, accessibility, functionality, visual design, information architecture, and interactive elements. It aims to create a positive and meaningful experience for users by understanding their needs, goals, and behaviors. The goal of UX design is to ensure that the user's journey is intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable.
Key aspects of user experience include:
- Usability: The product or interface should be easy to use, navigate, and understand. It should be intuitive, with clear instructions and minimal learning curve. Usability testing and user research help identify areas of improvement in this regard.
- Visual Design: The visual aesthetics, layout, and overall design of the interface should be visually appealing and coherent with the brand identity. It should also enhance the user's understanding and interaction with the product.
- Information Architecture: The structure and organization of information should be logical and intuitive. Users should be able to find what they're looking for quickly and easily, without feeling overwhelmed or confused.
- Interaction Design: This focuses on designing interactive elements such as buttons, menus, forms, and other interactive components. The interactions should be smooth, responsive, and consistent, providing feedback to users and guiding them through their tasks.
- Accessibility: The product or interface should be accessible to users of diverse abilities, including those with disabilities. It involves considering factors such as color contrast, text size, assistive technologies, and alternative navigation options.
- Emotional Design: This aspect considers the emotional response and connection that users have with the product or interface. It aims to create positive emotions, delight, and satisfaction through the design elements, copywriting, and overall experience.
By prioritizing user experience, businesses and designers can create products that meet user needs, solve their problems, and ultimately foster customer satisfaction and loyalty. User research, usability testing, and iterative design processes are often employed to continuously improve and refine the user experience based on user feedback and data.

What is the User Journey?
The user journey, also known as the user flow or user pathway, refers to the sequence of steps or interactions that a user takes when engaging with a product, service, or website. It illustrates the path that users follow to achieve their goals or complete specific tasks within a system.
The user journey typically encompasses the following elements:
- Entry Point: This is the starting point of the user's journey, where they first encounter the product or service. It could be a landing page, a search engine result, a social media post, or any other entry point.
- Actions and Interactions: Users engage with the product or service by performing various actions and interactions. These can include clicking buttons, filling out forms, navigating menus, viewing content, making selections, and more.
- Pathways: Users navigate through different pages or screens, following specific pathways based on their goals and the options provided. The user journey may involve branching paths, depending on the choices made by the user.
- Decision Points: Users may encounter decision points where they have to make choices or select options that impact their journey. These decisions can determine the subsequent steps and outcomes.
- Exit Point: The user journey concludes when the user achieves their goal or decides to exit the product or service. This could involve completing a purchase, submitting a form, signing up for a newsletter, or simply leaving the website or app.
Understanding the user journey is crucial for designing and optimizing the user experience. By mapping out the user journey, designers and product teams can identify pain points, areas of confusion, and opportunities for improvement. This helps them create more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces, streamline processes, and ensure that users can accomplish their tasks effectively and efficiently.
Introduction to ISO/IEC 27001 and its benefits
ISO/IEC 27001 is a standard for information security management systems (ISMS). It provides benefits such as compliance with regulations, increased revenues, lowering expenses, and better organization.
Key concepts, part of the standard, include confidentiality, integrity, and availability. These concepts are applied in ISO/IEC 27001 to protect information assets.
The standard describes key roles such as Top management, information security manager, and other stakeholders that have specific responsibilities in implementing and maintaining an ISMS based on ISO/IEC 27001. ISO/IEC 27001 provides guidance on implementing and maintaining an effective ISMS to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
ISO/IEC 27001 includes a process for identifying and assessing information security risks, as well as developing and implementing risk management strategies. Risk management consists of risk assessment (finding out which risks exist and how big they are) and risk treatment (defining how to deal with risks). Risk management is a crucial concept in ISO/IEC 27001 because this is the main method to find out how company sensitive information can be endangered, and to define which controls (safeguards) to use to deal with those risks.
The standard includes safeguards and measures to be implemented to protect information assets from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. They can include physical controls, technical controls, and administrative controls.
The standard describes processes and procedures that must be in place to detect, respond to, and manage information security incidents. It involves identifying and containing incidents, investigating their causes, and implementing corrective actions to prevent future incidents.
Another key aspect of the standard is the concept of continual improvement and monitoring of the ISMS. This involves regularly monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the information security management system (ISMS) and implementing improvements as necessary. It ensures that the ISMS remains up-to-date and aligned with changing risks and business needs.

To support the continuous improvement activities, the internal audits are described and are systematic assessments of the ISMS to determine its compliance with ISO/IEC 27001 requirements and identify areas for improvement. Management reviews involve top management evaluating the performance of the ISMS and making decisions for its improvement.
The ISO/IEC 27001 standard also covers other requirements the organization could require to be compliant with. This refers to ensuring that the organization's information security practices and controls align with applicable laws, regulations, and contractual obligations. It involves identifying and understanding relevant requirements and implementing measures to achieve compliance.
If you need help implementing or improving an ISMS based on the ISO/IEC 27001 standard or other standard, contact us, our team of specialists will be happy to help you.
Setting up or improving a performance management system
Ensuring the proper setting of a business performance system involves careful planning, consideration of key factors, and a strategic approach. Here are steps and considerations to help you establish an effective business performance system:
- Involve Stakeholders
Engage key stakeholders, including executives, managers, and frontline employees, in the development of the performance system. Consider their perspectives and ensure buy-in at all levels. - Define Clear Objectives
Clearly articulate the objectives and goals of your business performance system.
Understand what you aim to achieve and how it aligns with the overall business strategy. - Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify and define the key performance indicators that are relevant to measuring your business objectives. These should be measurable, specific, and directly tied to your business strategic goals.
Ensure that the chosen KPIs align with the broader business strategy. The performance system should reflect the priorities and focus areas outlined in the strategic plan. - Establish Data Collection and Measurement Processes
Define the processes for collecting and measuring data related to the selected KPIs.
Ensure data accuracy, reliability, and consistency to make informed decisions. - Select Appropriate Technology
Choose technology platforms or tools that support data collection, analysis, and reporting. The selected technology should align with the needs of your organization and facilitate seamless integration with existing systems. - Set Realistic Targets and Benchmarks
Establish realistic performance targets and benchmarks.
Ensure that these are challenging yet achievable, providing motivation for improvement without creating unattainable expectations. - Implement a Performance Management Framework
Develop a performance management framework that outlines roles, responsibilities, and processes for performance evaluation and improvement. - Promote Continuous Monitoring
Implement continuous monitoring mechanisms to track performance in real-time.
Regularly review KPIs and performance metrics to identify trends and areas for improvement. - Encourage a Data-Driven Culture
Foster a culture that values data-driven decision-making.
Encourage employees to use performance data to inform their actions and contribute to continuous improvement.

- Provide Training and Support
Offer training to employees on the use of the performance system.
Ensure that users understand how to interpret data and take actions based on performance insights. - Regularly Review and Adjust
Schedule regular reviews of the performance system.
Assess the effectiveness of KPIs, data collection processes, and overall system performance.
Adjust as needed to stay aligned with evolving business strategic goals. - Communicate Results and Insights
Communicate performance results and insights throughout the organization. Transparency in reporting fosters accountability and awareness of performance expectations. - Communicate Results and Insights
Communicate performance results and insights throughout the organization. Transparency in reporting fosters accountability and awareness of performance expectations. - Comply with Regulations and Standards
Ensure that the business performance system complies with relevant regulations and industry standards. This may include data privacy and security considerations.
By following these steps and considering these aspects, you can establish a robust business performance system that supports your strategic objectives, engages stakeholders, and contributes to continuous improvement in your organization.
If you need help implementing or improving a performance management system, contact us, our team of specialists will be happy to help you.
Compliance Service Offering for Law 25
To support our clients who need to adjust their strategic and operational approaches and to meet the requirements of Law 25, we offer a compliance service.

The six main components of our personal information governance service offering to comply with Law 25 are:
1. Personal Information Governance
- Establishment of a governance framework
- Determination of governance rules
- Development of governance policy
- Development of privacy policy
- Accountability
2. Personal Information Management
- Inventory
- Their processing throughout their lifecycle
- Their protection/security
3. Management of Data Subject Rights
- Handling requests
- Handling complaints
4. Management of Privacy Incidents
5. Management of Projects Involving Personal Information
- Conducting Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs)
6. Training and Awareness Program on Personal Information Protection

